REGENERATIVE THERAPIES
In recent years, advances in healthcare research have led to new treatments that utilise the body’s natural healing mechanisms. Known as regenerative therapies, these are increasingly used in treating conditions that are not responsive to traditional care techniques.
What are Regenerative Therapies?
These therapies have an anti-inflammatory affect, provide pain relief and encourage healing in damaged tissues. Compared with other methods such as cortisone injections and oral anti-inflammatories, these treatments have been shown to be safer and more effective in treating numerous podiatric conditions involving damaged tissue.
wHAT CONDITIONS CAN THEY HELP TREAT?
Conditions that can respond well to regenerative therapies include:
- Plantar fascia tears, Achilles Tendon tears, Peroneal tendon tears, Tendon sheath inflammation.
- Osteoarthritis of knee, ankle, big toe and other foot joints.
- Stubborn soft tissue injuries that do not respond to conventional treatments - eg. Achilles tendinopathy, plantar fasciitis, peroneal tendinopathy, ankle sprains
- Fractures, stress fractures, talar dome lesions.
- ATFL(ankle ligament) tears from ankle sprains, acute and chronic ankle conditions .
- Lymphedema of the leg, Morton’s neuroma, plantar plate injuries, diabetic wounds
- Nerve entrapment and neuropathic pain- common nerves affected include common fibular, superficial fibular, and sural.
- Post-surgical nerve pain, or damage
- Complex regional-pain syndromes, and other pain conditions.
These therapies can also speed up healing after surgery. Injections are often guided with ultrasound to ensure accurate placement.
Depending on the patient’s individual needs and condition, they are often combined with other podiatric treatments or biomechanical supports such as paddings, tapings, orthotics and footwear adjustments.
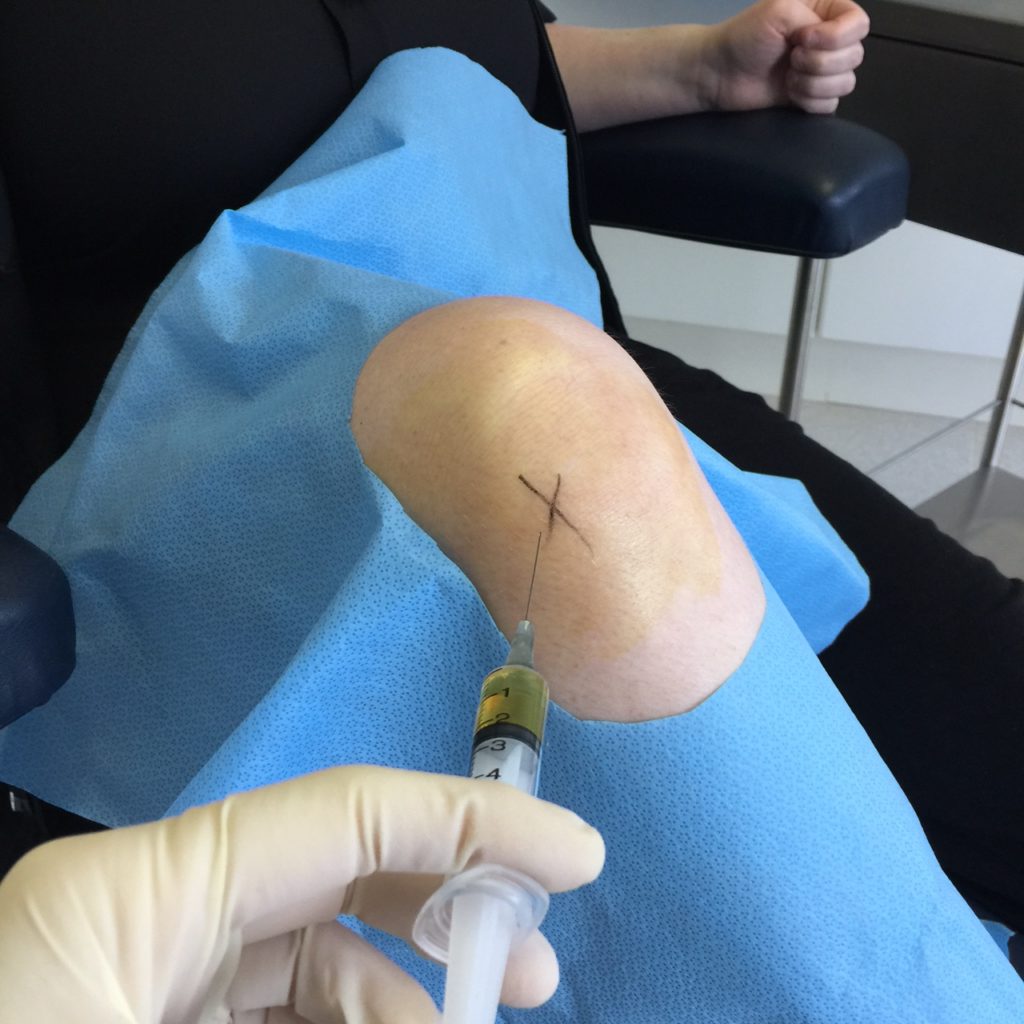
What therapies are offered?
Cheltenham Podiatry’s in-house regenerative therapy clinic offers a number of cutting-edge, drug free treatments. Head podiatrist Jacqueline Kan is proud to be the first podiatrist in Melbourne to offer some of these therapies, such as platelet rich plasma. All therapies are carried out by highly trained and qualified practitioners. A continually growing body of evidence supports the efficacy and safety of these treatments.
Regenerative therapies we offer include injection therapies as : Prolotherapy this includes both Classic and Neural Prolotherapy (Perineural Injection Therapy), Orthobiologics (Platelet Rich Plasma and Cytokines). Other Regeneratine treatments that are used separately or combines with these include Photobiomodulation and Shockwave therapy.
Book an appointment
FIND OUT MORE
To learn more about these therapies and find out if they’re right for you, make a booking with Cheltenham Podiatry today.
You can book online now, or call us on 03 9583 3093 to speak to our friendly team.


© Copyright 2025, Cheltenham Podiatry | SBM


